UK university grades explained
This article will help you understand how university grades and classifications work. You can find out about:
Undergraduate degrees
Qualifications in England, Wales and Northern Ireland are categorised into qualification levels. This is according to the Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF). An undergraduate degree is considered anything from Level 4 to Level 6 on the RQF.
Undergraduate degrees are usually taught at universities. They involve studying one or more subject in detail. There are different types of undergraduate degrees that you can study. The amount of time you study will depend on your type of qualification.
Undergraduate degree classifications

Postgraduate degrees
A postgraduate degree is an advanced qualification. They are usually studied after completing an undergraduate degree. Postgraduate qualifications are usually Level 7 and Level 8 on the Regulated Qualification Framework. Some graduate level qualifications are Level 6.
You can study for a taught postgraduate qualification, or you may wish to study a postgraduate research course. Taught postgraduate qualifications include master’s degrees and postgraduate diplomas (PGDip) or certificates (PGCert).
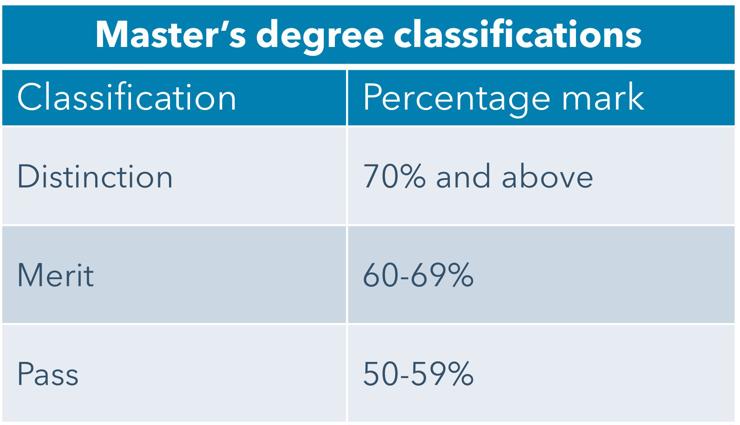
Postgraduate degree classifications
Postgraduate research degree classifications
A postgraduate research degree usually involves working on a single in-depth research project. It’s for those considering a career in academia or research. Typically they are studied after completing a bachelor’s or master’s degree. They are not graded in the same way as taught postgraduate degrees. You either pass or fail, with recommendations for improvement.
How university grades are calculated
The way university grades are calculated depends on your course and the institution you’re studying at. You should check your university's academic regulations for full information.
